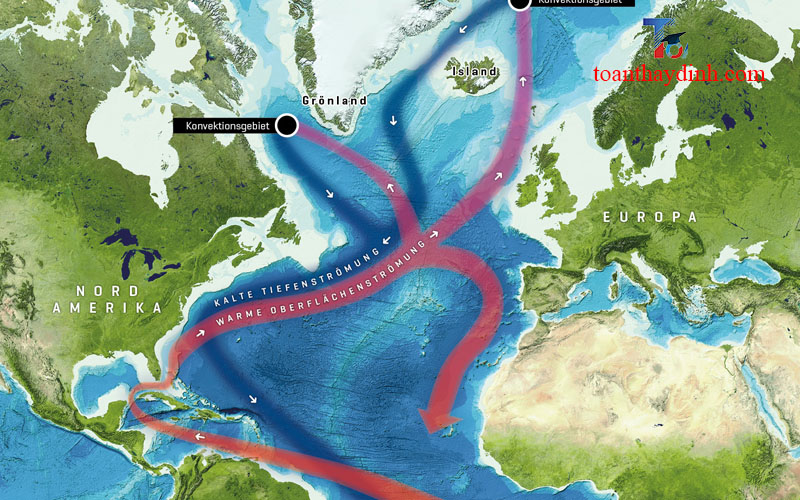
The Gulf Stream climate change, a powerful warm ocean current originating in the Gulf of Mexico, has been subject to increasing concerns regarding the impacts of climate change. As global temperatures rise and ice sheets melt, scientists worry about potential disruptions to this vital oceanic conveyor belt. The Gulf Stream plays a crucial role in regulating weather patterns and maintaining the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. In this article, we delve into the effects of climate change on the Gulf Stream and explore the potential consequences for our planet’s climate system.
The Gulf Stream climate change is a powerful ocean current that flows along the eastern coast of the United States and crosses the Atlantic Ocean towards Europe. It is one of the most significant currents in the world and has a tremendous impact on global climate patterns. The Gulf Stream is a complex and dynamic system that plays a crucial role in the distribution of heat around the planet. Understanding its characteristics, functions, and importance is essential for comprehending the intricate workings of our climate system.
Mục lục
Definition of the Gulf Stream

The Gulf Stream climate change can be defined as a warm and swift ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico. It enters the Atlantic Ocean through the Straits of Florida and flows northward along the eastern coast of the United States. The Gulf Stream is part of the larger Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) system, which includes several interconnected currents.
This powerful current is fueled by a combination of various factors, including the temperature and salinity differences between the Gulf Stream and the surrounding waters. The warm waters of the Gulf Stream, with their higher salt content and relatively faster speed, contrast with the colder and less saline waters of the North Atlantic, generating a stark boundary known as the Gulf Stream front.
Importance of the Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream plays a fundamental role in maintaining the climate equilibrium of regions it influences. Its warm waters transport enormous amounts of heat energy from the tropics towards the higher latitudes, significantly affecting the weather patterns along its path. The impact of the Gulf Stream extends beyond the coastal areas it directly affects, influencing climate systems globally.
One of the key functions of the Gulf Stream is the redistribution of heat from the equator towards the poles. This process helps to regulate and moderate temperatures in regions that lie in the path of the current. As the warm Gulf Stream waters flow northward, they release heat, warming the surrounding atmosphere and contributing to the temperate climate experienced by countries like the United Kingdom, Ireland, and Scandinavia.
Furthermore, the Gulf Stream climate change influences weather systems, oceanic currents, and marine ecosystems along its route. It acts as a highway for the transport of nutrients, plankton, and fish larvae, creating a rich and diverse marine environment. The migration patterns of marine species are also influenced by the Gulf Stream, as it provides an essential corridor for their movements.
The Gulf Stream also has profound implications for global climate and weather patterns. It affects the position and intensity of atmospheric jet streams, which play a crucial role in weather systems and storm formation. Changes in the Gulf Stream’s strength or position can influence the frequency and severity of storms, and alter precipitation patterns in regions far beyond its reach.
With the increasing concerns regarding climate change, understanding the impact of the Gulf Stream has become even more critical. Changes in the intensity and stability of the Gulf Stream can have far-reaching consequences on weather patterns and oceanic systems worldwide. Scientists are studying potential correlations between the Gulf Stream and climate change, assessing the potential impacts of warmer ocean temperatures on the strength and stability of this crucial current.
In conclusion, the Gulf Stream is a significant oceanic current with a vast influence on climate patterns and ecosystems. Its warm and swift waters transport heat energy from the tropics towards higher latitudes, affecting weather systems and maintaining a temperate climate in regions it influences. The Gulf Stream also plays a crucial role in the productivity of marine ecosystems, as well as in the redistribution of nutrients and species migration. Understanding the Gulf Stream climate change characteristics and functions is vital for comprehending the intricate workings of our climate system and anticipating potential impacts of climate change on this crucial current.
Factors Influencing Climate Change in the Gulf Stream
Global Warming and Rising Temperatures
The Gulf Stream climate change is a crucial ocean current system that flows in the Atlantic Ocean, primarily impacting the eastern coastline of North America and the western coastline of Europe. This important current is influential in shaping climate patterns, weather conditions, and overall oceanic circulation. However, various factors are contributing to climate change in the Gulf Stream, with global warming and rising temperatures being one of the most significant.
Global warming, largely fueled by human activities such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, leads to an overall increase in temperatures worldwide. As the Earth’s atmosphere traps more heat, the surface temperature of the ocean increases as well. This rise in temperature directly affects the Gulf Stream climate change and its surrounding waters. Warmer waters can disrupt the delicate balance of the current, altering its strength and direction, which consequently impacts the climate of coastal regions influenced by the Gulf Stream.
Furthermore, these rising temperatures have other adverse effects on the Gulf Stream climate change. One of the key consequences is the accelerated melting of ice from polar regions and glaciers. As the polar ice caps and glaciers melt, the influx of fresh water into the ocean disrupts the normal salinity levels in the Gulf Stream. Changes in salinity can weaken the current, affecting its ability to transport warm water from the tropics to the higher latitudes. The weakened Gulf Stream not only impacts the climate but also affects important ecosystems and marine life that rely on the current for their survival.
The implications of global warming and rising temperatures on the Gulf Stream’s climate-altering capabilities are substantial. A weakened current could potentially result in altered weather patterns along the East Coast of the United States and Europe, including changes in precipitation levels, temperature extremes, and storm frequency. The increased intensity and frequency of hurricanes and tropical storms witnessed in recent years can be partially attributed to the changes in the Gulf Stream caused by global warming.
Changes in Ocean Currents and Circulation Patterns
In addition to global warming, another significant factor influencing climate change in the Gulf Stream is the alteration of ocean currents and circulation patterns. The Gulf Stream is part of a global system of interconnected ocean currents, known as the Thermohaline Circulation, which plays a vital role in distributing heat around the planet.
One key aspect of this circulation is the sinking of dense, cold water in the North Atlantic, which helps drive the Gulf Stream. However, research suggests that climate change can disrupt this process by increasing the influx of freshwater from melting ice, as mentioned earlier. The excess freshwater reduces the density of the water, inhibiting its sinking and subsequently weakening the Gulf Stream.
Changes in ocean currents and circulation patterns not only impact the Gulf Stream but also have far-reaching consequences for global climate. The Gulf Stream is responsible for transporting warm water to higher latitudes, helping regulate temperatures and influencing weather conditions. If the current weakens or shifts significantly, it can disrupt the delicate balance of heat distribution, leading to abnormal temperature variations and altered weather patterns in regions influenced by the Gulf Stream.
The repercussions of these changes are not limited to coastal areas but can also have global effects. Alterations in the Gulf Stream’s climate-altering capabilities can lead to significant changes in precipitation patterns, affecting agriculture, water availability, and overall climate stability. For instance, regions accustomed to a moderate and relatively stable climate due to the Gulf Stream’s influence may experience more extreme and unpredictable weather events, including droughts or heavy rainfall.
In conclusion, climate change in the Gulf Stream is influenced by various factors, with global warming and rising temperatures being a primary driver. The increased temperatures lead to the melting of polar ice, disrupting the salinity levels and weakening the Gulf Stream. Furthermore, alterations in ocean currents and circulation patterns, caused by factors such as excess freshwater from melting ice, also contribute to climate change in the Gulf Stream. Understanding and addressing these factors are essential for mitigating the adverse effects of climate change on the Gulf Stream’s climate-altering capabilities and the ecosystems and communities it impacts.
Impact of Gulf Stream Climate Change

The Gulf Stream climate change is a strong, warm current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows along the eastern coast of North America before crossing the Atlantic Ocean towards Europe. It plays a crucial role in the Earth’s climate system, distributing heat and nutrients and influencing weather patterns. However, the Gulf Stream is vulnerable to climate change, and its potential slowing or shutdown could have significant impacts on ecosystems, biodiversity, sea levels, and coastal flooding.
Shifts in Ecosystems and Biodiversity
The Gulf Stream climate change acts as a highway for marine species, transporting them across thousands of kilometers of ocean. Changes in the strength or path of the Gulf Stream could disrupt these migrations and result in shifts in ecosystems and changes in biodiversity. Warmer waters carried by the Gulf Stream provide habitats for a wide variety of marine life, including commercially important fish species. If the Gulf Stream weakens, these species may need to move further north to seek suitable thermal conditions, which could affect fishing industries and pose challenges to already vulnerable populations.
Additionally, the Gulf Stream climate change delivers vital nutrients from the deep ocean to surface waters, fueling the growth of phytoplankton, the foundation of marine food webs. Phytoplankton, in turn, supports the entire marine ecosystem. The alteration or slowdown of the Gulf Stream could disrupt this nutrient supply chain, leading to changes in phytoplankton distribution and abundance, which would cascade through the food web and impact higher trophic levels, including fish, marine mammals, and seabirds.
Sea Level Rise and Coastal Flooding
Gulf Stream climate change is causing global sea levels to rise as ice sheets and glaciers melt, but the Gulf Stream could exacerbate this effect along the eastern coast of North America. The warm Gulf Stream waters tend to be higher than their surrounding environment, creating a ‘bulge’ in sea level known as a ‘thermal expansion.’ This bulge, combined with the rising sea levels due to climate change, increases the risk of coastal flooding and storm surges.
If the Gulf Stream climate change weakens or changes its path, it could alter the distribution of warm waters along the coast, affecting the intensity and frequency of storms and their accompanying surges. These changes in coastal dynamics can have devastating effects on human settlements, infrastructure, and natural habitats. Low-lying coastal areas, such as barrier islands and estuaries, are particularly vulnerable to flooding and erosion under these circumstances.
It is worth noting that the impact of Gulf Stream climate change is not restricted to the North American and European coasts. The Gulf Stream also influences weather patterns, including the transport of heat and moisture, which significantly affect climate across large areas of land. Changes in the Gulf Stream could therefore have far-reaching consequences, including altered rainfall patterns, temperature regimes, and the occurrence of extreme weather events.
Gulf Stream climate change can have wide-ranging impacts on ecosystems, biodiversity, sea levels, and coastal flooding. The potential weakening or shutdown of the Gulf Stream can alter marine migrations, disrupt nutrient supply chains, and threaten commercially important fish species. Furthermore, it can contribute to increased coastal flooding, exacerbating the risks associated with rising global sea levels. Understanding and mitigating these impacts is critical to safeguarding both human and ecological communities that depend on the Gulf Stream’s current. By recognizing the importance of this issue and taking appropriate action, we can strive to protect and preserve this crucial component of our planet’s climate system.
Implications on Weather Patterns

The implications of Gulf Stream climate change on weather patterns are vast and have significant consequences for our planet. One of the areas where climate change has a notable impact is on the intensity of storms. Additionally, climate change also alters rainfall patterns, leading to changes in precipitation distribution and frequency.
Increased Intensity of Storms
Gulf Stream climate change has been linked to an increase in the intensity of storms around the world. Warmer temperatures are a key driver behind this phenomenon. As global temperatures rise, the energy available to fuel storms also increases. This increase in energy can result in more powerful hurricanes, typhoons, and other extreme weather events.
One of the regions where the increased intensity of storms is most evident is the Gulf Stream climate change. The Gulf Stream is a powerful ocean current that influences the climate of the eastern coast of North America and Western Europe. With climate change, the Gulf Stream is not immune to the impacts of warming temperatures. As the global climate becomes hotter, the Gulf Stream may also experience changes that could further intensify storms in the region. This could mean more frequent and stronger hurricanes hitting coastal areas along the Gulf Stream.
It is important to note that the implications of climate change on storm intensity are not restricted to the Gulf Stream climate change alone. Storms all over the world, from the Pacific to the Indian Ocean, are projected to become more intense due to the effects of climate change. In fact, recent studies suggest that the frequency of the most intense storms, such as Category 4 and 5 hurricanes, could increase as the planet warms. These storms can cause devastating damage to coastal communities and ecosystems.
Altered Rainfall Patterns
Gulf Stream climate change also disrupts historical rainfall patterns, leading to shifts in the timing, distribution, and amounts of precipitation. These alterations in rainfall patterns have significant implications for agriculture, water resources, and ecosystems. Changes in rainfall can result in both increased droughts in some areas and increased flooding in others.
The Gulf Stream climate change region, for example, may experience altered rainfall patterns due to climate change. It is projected that warmer ocean temperatures and shifting atmospheric circulation patterns could lead to changes in the precipitation regime along the Gulf Stream. This could result in increased rainfall in certain areas, especially in regions already prone to heavy rainfall, while simultaneously causing drier conditions elsewhere.
The consequences of altered rainfall patterns can be far-reaching. Agriculture heavily relies on predictable moisture availability, and changes in precipitation timing and amounts can disrupt crop cycles and reduce yields. Water resources are also impacted, as altered rainfall patterns can affect the recharge of groundwater, river flows, and reservoir levels. Moreover, ecosystems that depend on specific rainfall patterns may suffer, leading to changes in vegetation, biodiversity, and the overall functioning of ecosystems.
Gulf Stream climate change has profound implications for weather patterns worldwide. Increased storm intensity and altered rainfall patterns are two of the key consequences of a changing climate. The Gulf Stream climate change, specifically, may experience these changes, with potential implications for the intensity of storms and the distribution of rainfall in the region. It is crucial that we continue to monitor and study these effects to better understand and mitigate the impacts of Gulf Stream climate change on weather patterns, ensuring the resilience of our communities and ecosystems in the face of a rapidly changing climate.
Efforts to Mitigate Gulf Stream Climate Change
The Gulf Stream climate change is a powerful ocean current that plays a significant role in regulating the global climate system. It transports warm water from the Gulf of Mexico up towards the North Atlantic, influencing weather patterns and maintaining the temperature balance in the region. However, the Gulf Stream and its associated climate systems are under threat due to human-induced climate change. Rising greenhouse gas emissions and unsustainable fishing practices are among the key factors contributing to this issue. In response, various efforts are being made to mitigate the impacts of Gulf Stream climate change.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions
One of the most crucial steps in mitigating Gulf Stream climate change is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial activities are the primary sources of these emissions. Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the major greenhouse gas contributing to global warming and ocean acidification, both of which affect the Gulf Stream’s stability and functionality. To combat this, governments, industries, and individuals need to adopt cleaner and more sustainable practices.
In the energy sector, transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power can significantly reduce CO2 emissions. Investing in clean energy infrastructure and improving energy efficiency in buildings are also important steps. Governments can play a crucial role by implementing policies that promote renewable energy adoption and incentivize the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, individuals can contribute by making sustainable choices such as using public transportation, driving electric vehicles, and reducing energy consumption.
Addressing deforestation is another key aspect of reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. However, widespread deforestation results in the release of stored carbon, exacerbating climate change. Efforts to mitigate Gulf Stream climate change should include measures to protect and restore forests globally. This can be achieved through stricter regulations on logging, promoting sustainable land use practices, and supporting reforestation initiatives.
Promoting Sustainable Fishing Practices
Unsustainable fishing practices also pose a significant threat to the Gulf Stream climate change and its associated ecosystems. Overfishing, destructive fishing methods, and bycatch contribute to the decline of fish populations, disrupt food chains, and disturb the overall balance of the marine environment. To mitigate these impacts, it is crucial to promote sustainable fishing practices.
Implementing and enforcing regulations that limit fishing quotas and protect vulnerable species can help preserve the biodiversity of the Gulf Stream climate change. Scientific research plays a vital role in understanding fish populations and their habitats, enabling informed management decisions. Collaborative efforts between scientists, governments, and the fishing industry can lead to the development of sustainable fishing practices that ensure the long-term viability of marine ecosystems.
Adopting more selective fishing gear and techniques is essential to minimize bycatch, which refers to unintentional capture of non-targeted species. Bycatch can have detrimental effects on marine populations, including endangered species and marine mammals. Encouraging the use of innovative fishing gear that reduces bycatch, such as circle hooks and fish excluder devices, can significantly mitigate the negative impacts on the Gulf Stream and its biodiversity.
Education and awareness also play a crucial role in promoting sustainable fishing practices. By informing the public about the importance of responsible fishing and consumer choices, individuals can make informed decisions when purchasing seafood products. Sustainable seafood certifications and labels can help consumers identify products that have been caught using environmentally friendly practices. Collaboration between government bodies, non-governmental organizations, and the fishing industry can help develop educational programs and campaigns that drive positive change.
In conclusion, mitigating Gulf Stream climate change requires a comprehensive approach that addresses both greenhouse gas emissions and unsustainable fishing practices. Reducing emissions through the transition to renewable energy sources and protecting forests is crucial for stabilizing the global climate system. Promoting sustainable fishing practices, including limiting fishing quotas, minimizing bycatch, and raising public awareness, is essential for preserving the biodiversity of the Gulf Stream Climate change and its associated ecosystems. By combining these efforts, we can work towards mitigating the impacts of Gulf Stream climate change and safeguarding this vital ocean current for future generations.
Understanding and Addressing the Challenges Ahead
As we conclude this discussion on the challenges and impacts of climate change, it is crucial to emphasize the significance of understanding and addressing these issues. The Gulf Stream Climate change, an essential ocean current in the Atlantic Ocean, plays a fundamental role in regulating weather patterns and climate in various regions. However, it is under threat due to the effects of climate change.
The Gulf Stream Climate change, also known as the North Atlantic Drift, is a powerful current that carries warm water from the Gulf of Mexico up along the eastern coast of the United States and across the Atlantic Ocean towards Europe. This current has a significant influence on the climate of the surrounding areas. It helps to maintain the relatively mild temperatures experienced in regions like the United Kingdom and Western Europe, despite their high latitudes. The Gulf Stream Climate Change also affects the strength and frequency of hurricanes in the Atlantic Ocean, impacting coastal communities.
However, climate change poses a significant risk to the stability of the Gulf Stream. Rising global temperatures lead to the melting of polar ice caps, resulting in increased freshwater entering the North Atlantic. This influx of freshwater disrupts the delicate balance of saltwater and can weaken or even shut down the Gulf Stream Climate change. Such an event would have severe consequences for weather patterns and climate stability in affected regions, potentially leading to more extreme weather events and altering ecosystems.
To address the challenges posed by climate change, it is vital to take immediate action in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and adopting sustainable practices. By mitigating the causes of climate change, we can help to preserve the stability of the Gulf Stream and minimize its potential disruption. International cooperation and commitment are essential, as climate change is a global issue that requires a collective effort to address effectively.
Furthermore, investing in research and understanding the complex dynamics of the Gulf Stream and its interaction with climate change is crucial. Scientists and researchers have been studying the potential impacts of a weakened or disrupted Gulf Stream, but a more comprehensive understanding is necessary to develop accurate predictive models and inform policymakers. This knowledge can guide adaptation strategies and help communities prepare for potential changes in weather patterns and coastal dynamics.
Public awareness and education are also key components in addressing the challenges ahead. By informing the public about the importance of the Gulf Stream and its vulnerability to climate change, we can encourage individuals and communities to take action. This can range from supporting renewable energy initiatives to participating in coastal cleanup efforts and advocating for policy changes that prioritize climate action.
The Gulf Stream Climate Change is a critical system that regulates weather patterns and climate stability in various regions. However, the impacts of Gulf Stream Climate change pose a threat to its stability and functionality. Understanding and addressing the challenges ahead are necessary to mitigate the risks associated with a weakened or disrupted Gulf Stream. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, investing in research, and promoting public awareness, we can work towards preserving the Gulf Stream and creating a more sustainable future for generations to come. Addressing the challenges of Gulf Stream Climate change is not only essential for the Gulf Stream Climate change but for the overall well-being of our planet.
Trend –